The annual statement
of expenditures and tax revenues of a government during a particular period is called
federal budget. The
federal budget finances, the activities of the government and is used to achieve
higher level of national income and employment without inflation in the country. When the expenditures of the government are higher than its revenue during a
particular period of one year, the government has a deficit budget. If
the government expenditures are less than the tax revenues, the government has a
budget surplus. In case the government expenditures are equal to tax revenues,
the government has a balanced budget. When the federal budget is in deficit, the government has to borrow to
finance the deficit between expenditures and receipts. The accumulated
outstanding debt of the Federal government is called the national debt.
We can describe national debt
as the sum of all the past federal deficits.
In the words of Karl
E. Case:
"National debt is the total of all accumulated federal
deficit minus surpluses overtime".
National Debt and Determination of
National Income:
The classical economists were of the view has if the economy is left on its
own and there is no government interference in economic matters, it has a
natural tendency to move towards equilibrium, of full employment without
inflation.
The Keynesian economics reject the classic economics based on
competitive market's flexible prices. It emphasizes the possibility that an
economy can be in equilibrium or less than full employment or above the level of
full employment with inflation. The Keynesian economics stresses that fiscal
policy (government intervention) can bring the economy at full employment
equilibrium without inflation. The goal can be achieved by managing aggregate
demand.
The increase in aggregate demand can be brought about by adopting
expansionary
fiscal policies and decrease in aggregate in demand by contractionary fiscal
policies tax cuts and government spending increases the aggregate demand for
goods and services (expansionary fiscal policies) and tax increases and
reduction in government spending decrease the aggregate demand (contractionary
fiscal policies).
When the government increases its spending to stimulate the economy, its
budget deficit increases. If the budget deficits continue to increase overtime,
the national debt burden increases. The increase in government expenditure
through budget deficit is undertaken to curb recession. The government here has
a choice. It can increase revenue by raising taxes. This method is not
effective, because the rise in taxes reduces the disposable income of the people
and hence fall in demand for goods. The government, therefore, has no other
alternative but to resort to budget deficits if expansionary effect in the
economy is to be realized.
In recession, the government spends the borrowed amount from internal or
external resources by undertaking public works program on a large scale. The
undertaking of the public works programs raises the personal incomes of the
households and business firms which lead to higher consumption of goods and
services depending on marginal propensity to consume of the people. The increase
in demand for goods brings about expansion in output which further generates
employment and income via multiplier. The rise in income and as a consequence in
investment raises the aggregate demand for goods and shifts the aggregate demand
curve upward closing the recessionary gap till the equilibrium is established at
the full employment level. The effects of increase in government expenditure
through budget deficits for curing recession is now explained with the help of
diagram.
Diagram:
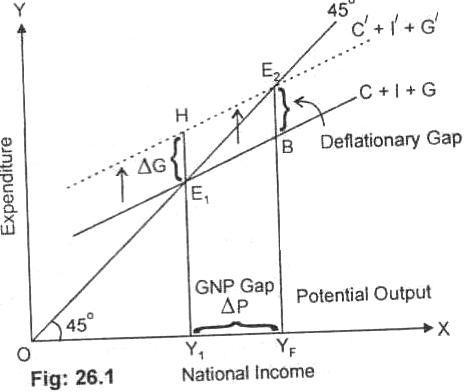
In the Fig. 26.1, it is shown that the aggregate demand curve C + I + G
intersects the 45° line at point E1. the equilibrium level of income is OY,
which we assume is below the full employment income OYF. There exists a capacity
in the economy for expansion. The economy is faced with deflationary gap equal
to E2B. If the government increases its expenditure by E1H, the aggregate
demand curve will shift upward to full employment level of