Effects of Changes in
Demand on Equilibrium Market:
We
know that if the price rises, other things remaining the same, people buy
less of that commodity and if price falls, people buy more of that commodity.
Let us now discuss the effects of changes in demand on
equilibrium price.
A change to
demand can take place independently of change in price, i.e., price remaining
the same, people may purchase more or less of the commodity. When larger
quantity is demanded at the same old price or the same old quantity is demanded
at a higher price we say, the demand has risen. In such a case, the whole of
demand curve rises above the original demand curve. In case of a fall in demand,
the whole of the demand curve falls below the original demand curve.
In order to
study the effect of the changes in demand on equilibrium price, let us assume
that no change takes place in the supply schedule, i.e., it remains fixed. If
demand rises, more quantity will be purchased at a higher price. On the other
hand, if demand falls, less commodity will be purchased at a lower price. This
can also be illustrated in the following diagram.
Diagram/Figure:
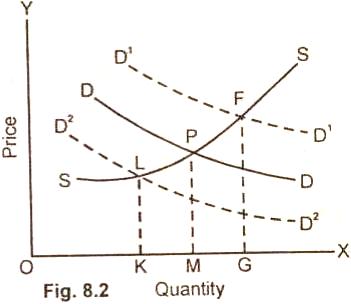
In the
figure (8.2) DD/ is the original demand curve. PM is the equilibrium price and OM the
equilibrium amount. When demand rises, supply remaining the same, the
equilibrium amount increases from OM to OG and the equilibrium price rises from
PM to FG. In case of fall of in demand, which is indicated by D2D2
curve, the quantity demanded decreases from OM to OK and the equilibrium price
falls from PM to LK.
Now a
question can be asked that when the demand rises, does it affect more on the
price or on the quantity of the commodity to be sold? The answer to this simple
question, is that if the supply is perfectly elastic, a rise in demand will
increase the quantity but will not affect the price. If the supply is perfectly
inelastic, then a rise in demand will affect the price but not the quantity.
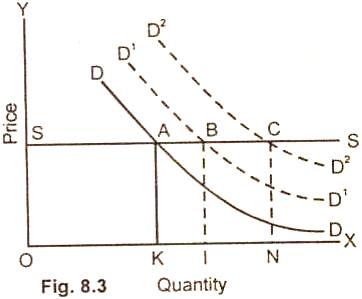
This can be shown with the help of the diagram. In case of perfect elastic
supply, (Fig. 8.3) when demand rises, the supply increases from OK to OI with
further rise in demand D2D2 the supply increases from OI
to ON.
Supply
Perfectly Inelastic:
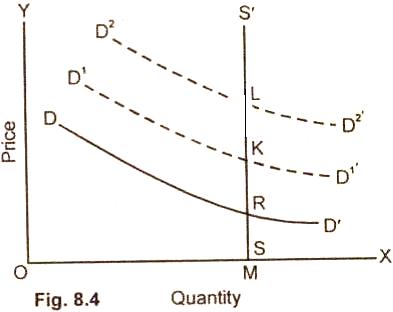
In fig. 8.4,
the supply is perfectly inelastic. A rise in demand affects the price which
rises from RM to KM and with the further rise in demand to LM. The quantity
supplied remains the same OM.
In the the
world in which we live, the supply is seldom perfectly elastic or perfectly
inelastic. It is either equal to unity or greater than unity, or less than
unity. We will, therefore, examine these, cases now. If elasticity of supply is
to unity and demand rises, the price and quantity will change in equal
proportion.
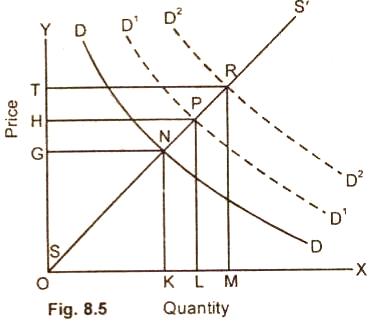
(i)
Elasticity of Supply is Equal to Unity:
The quantity and price change in
equal proportion with a rise in demand as is clear in fig. 8.5.
(ii)
Elasticity of Supply Greater Than Unity:
If the
elasticity of supply is greater than unity, a
rise in demand will affect the supply which will change in greater proportion
than the price as is obvious from the following fig. 8.6.
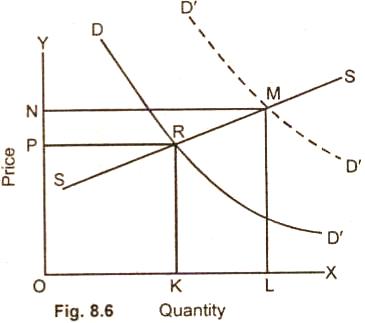
In fig. (8.6)
when demand rises, KL quantity supplied is greater in proportion than PN price.
(iii) Elasticity of Supply
Less Than Unity:
If the elasticity of supply is less
than unity, a rise in demand will change the price in greater proportion than
the quantity as shown in fig. 8.7.
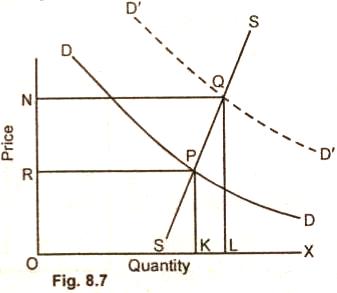
In fig. 8.7 the proportionate
change in quantity demanded KL is less than the change in price
RN.
Relevant Articles:
|