Long Run Equilibrium Under Monopoly:
The
monopolist creates
barriers of entry for the new firms into the industry. The
entry into the industry is blocked by having control over the raw materials
needed for the production of goods or he may hold full rights to the production
of a certain good (patent) or the market of the good may be limited. If new
firms try to enter in the field, it lowers the price of the good to such on
extent that it becomes unprofitable for new firms to continue production etc.
When
there is no threat of the entry of new firms into the industry, the monopoly
firm makes long run adjustments in the scale of plant. In case, the demand for
the product is limited, the monopolist can afford to produce output at sub
optimum scale. If the market size is large and permits to expand output, then
the monopolist would build an optimum scale of plant and would produce goods at
the minimum cost per unit. However, the monopolist would not stay in the
business, if he makes losses in the long period. The long run equilibrium of a
monopoly firm is now explained with the help of the following diagram.
Diagram/Curve:
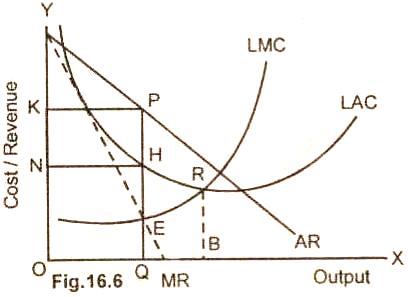
In the
long run, all the factors of production including the size of the plant are
variable. A monopoly firm will maximize profit at that level of output for which
long run marginal cost (MC) is equal to marginal revenue (MR) and the LMC curve
intersects the MR curve from below. In the figure (16.6), the monopoly firm is
in equilibrium at point E where LMC = MR and LMC cuts MR curve from below. QP is
the equilibrium price and OQ is the equilibrium output.
At OQ level of output,
the cost per unit is QH (LAC), whereas the price per unit of the good is QP. HP
represents the per unit super normal profit. The total super normal profit is
equal to KPHN. It may here be noted that at the equilibrium output OQ, the plant
is not being fully utilized. The long run average cost (LAC) is not minimum at
this level of output OQ. The firm will build an optimum scale of plant only if
the demand for the product increases.
Threat of Entry of New Firms:
If there is a threat of
entry of new firms into the market,
the monopolist adopts price reduction strategy. He instead of charging QP price
per unit, lowers the price to BR. Since the per unit price BR is equal to the
cost per unit at R, the monopoly firm is earning only normal profit in the long
run. The reduction in price and so in profits is adopted to prevent the entry of
new firms in the market.
Summing up, if a monopoly firm is in a position
to maintain its monopoly status, it can earn super normal profit in the long
period. However, if there is an effective threat of the entry of potential firms
in, the industry, then the firm can earn just normal profit by reducing the
price. The reduction in price depends on how strong is the threat of potential
entry into the industry.
Relevant Articles:
|