Movement Vs Shifts of Demand
Curve:
Changes in
demand for a commodity can be shown through the demand curve in two ways:
(1) Movement
Along the Demand Curve and (2) Shifts of the Demand Curve.
(1) Movement Along the Demand
Curve:
Demand is a
multivariable function. If income and other determinants of demand such as
tastes of the consumers, changes in prices of related goods, income
distribution, etc., remain constant and there is a change only in price of the
commodity, then we move along the same demand curve.
In this case, the demand
curve remains unchanged. When, as a result of change in price, the quantity
demanded increases or decreases, it is technically called extension and
contraction in demand.
The demand curve, which represents various price quantity has a negative slope.
Whenever there is a change in the quantity demanded of a good due to change, in
its price, there is a movement from one point price quantity combination to
another on the
same demand curve. Such a movement from one point price quantity combination to
another along the same demand curve is shown in figure (4.3).
Diagram/Figure:
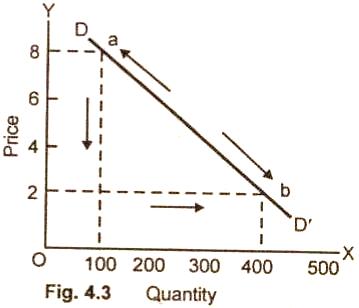
Here the
price of a commodity falls from $8 to $2. As a result, therefore, the quantity
demanded increases from 100 units to 400 units per unit of time. There is
extension in demand by 300 units. This movement is from one point price
quantity combination (a) to another point (b) along a given demand curve. On the
other hand, if the price of a good rises from $2 to $8, there is contraction in
demand by 300 units.
We, thus, see
that as a result of change in the price of a good, the consumer moves along the
given demand curve. The demand curve remains the same and does not change its
position. The movement along the demand curve is designated as change in
quantity demanded.
(2) Shifts in
Demand Curve:
Demand, as we
know, is determined by many factors. When there is a change in demand due to one
or more than one factors other than price, results in the shift of demand curve.
For example,
if the level of income in community rises, other factors remaining the same, the
demand for the goods increases. Consumers demand more goods at each price per
period of me (rise or Increase in demand). The demand curve shifts upward from
he original demand curve indicating that consumers at each price purchase more
units of commodity per unit of time.
If there is a
fall in the disposable income of the consumers or rise in the prices of close
substitute of a good or decline in consumer taste or non-availability of good on
credit, etc, etc., there is a reduction in demand (fall or decrease in demand).
The fall or decrease in demand shifts the demand curve from the original demand
curve to the left. The lower demand curve shows that consumers are able and
willing to buy less of the good at each price than before.
Schedule:
|
Pdx
($) |
Qdx |
Rise in Qdx |
Fall in Qdx |
|
12
|
100
|
300
|
50
|
|
6
|
250
|
500 |
200
|
|
4
|
500
|
600
|
300
|
Diagram/Figure:
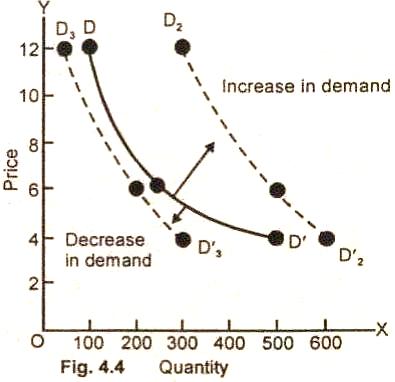
In this
figure, (4.4) the original demand curve is DD/.
At a price of $12 per
unit, consumers purchase 100 units. When price falls to$4
per unit, the quantity demanded increases to 500 units per unit of time. Let us
assume now that level of income increases in a community. Now consumers demand
300 units of the commodity at price of $12 per unit and 600 at price of $4 per
unit.
As a result, there is an upward shift of the demand curve DD2.
In case the community income falls, there is then decrease in demand at price of
$12 per unit. The quantity demanded of a good falls to 50 units. It is 300 units
at price of $4 unit per period of time. There is a downward shift of the demand
to the left of the original demand curve.
Summing Up:
(i)
Extension in demand is due to reduction in price.
(ii) Increase
in demand occurs due to changes in factors other than price.
(iii)
Contraction in demand is the result of a rise in the price commodity.
(iv) A decrease
in demand follows a change in factors other than price.
(v)
Changes in demand both increase and decrease are represent shifts in the
demand curve.
(vi)
Changes in the quantity demanded are represented by move along the same demand
curve.
Relevant Articles:
|