Monopolistic
competition refers to the market organization where there are a
fairly large number of firms which sell somewhat differentiated
products.
A single firm in the
product group (industry) has little impact on the market price.
However, if it reduces price, it can expect a considerable
increase in its sales. The firm may also attract buyers away
from other firms by creating imaginary or real difference
through advertising, branding and through many other sales
promotion measures (non-price
competition). If the firm raises its price, it will not lose
all its customers. This is because of the fact that the product
is differentiated from competing firms due to price and
non-price factors. The demand curve (AR curve) of the
monopolistic firm is therefore, highly elastic and is downward
sloping. As regards the marginal revenue curve, it slopes
downward and lies below the demand curve because price is
lowered of all the units to sell more output in the market.
Firm's Equilibrium Price and Output:
In the short-run, the
number of firms in the 'product
group' remains the same. The size of the plant of each firm
remains unaltered. The firm whether operating under perfect
competition, or monopoly wants to maximize profits. In order to
achieve this objective, it goes on producing a commodity so long
as the marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost. When MR =
MC, it is then in equilibrium and produces the best level of
output. If a firm produces less than or more than the MR = MC
output, it will then not be making maximum of profits.
In the short-run, a
monopolistically competitive firm may be realizing abnormal
profits or suffering losses. If it is earning profits, no new
firms can enter the industry in the short-run. In case, it is
suffering, losses but covering full variable cost, the firm will
continue operating so that the losses are minimized. If the full
variable cost is not met, the firm will close down in the
short-run. The short-run equilibrium with profits and short run
equilibrium with losses of a monopolistically competitive firm
are explained with the help of two separate diagrams as under.
Diagram:
In the figure (17.1),
the downward sloping demand curve (AR curve) is quite elastic.
The MR curve lies below-the average curve except at point N. The
SMC curve which includes advertising and sales promotional costs
is drawn in the usual fashion. The SMC curve cuts the MR curve
from below at point Z. The firm produces and sells an output OK,
as at this level of output MR = MC. The firm sells output OK at
OE/KM per unit price. The total revenue of the firm is equal to
the area OEMK, whereas the total cost of producing output OK is
OFLK. The total profits of the firm are equal to the shaded
rectangle FEML. The firm earns abnormal profits in the short
run.
Short
Run Losses:
If the demand and
cost situations are not favorable in the market, a
monopolistically competitive firm may incur losses in the
short-run. The short-run equilibrium of the firm with losses is
explained with the help of a diagram.
Diagram:
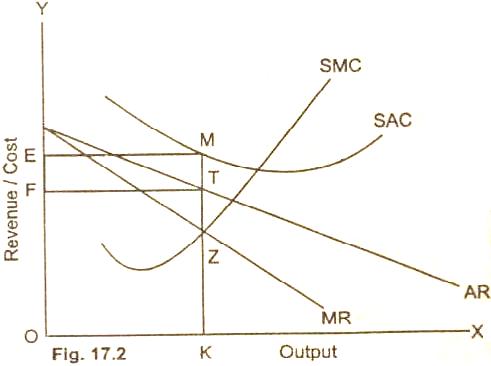
In the Figure (17.2),
marginal cost (SMC) equates marginal revenue MR curve from below
at point Z. The firm produces output OK and sells at OF/KT per
unit-price. The total receipt of the firm is OFTK. The total
cost of producing output OK is equal to OEMK. The firm suffers a
net loss equal to the area FEMT on the sale of OK output.