Determination of Short Run Normal Price
of Firm and Industry:
Definition:
In the short run, the size of a firm
and the number of firms comprising an industry remain the same.
The time is considered to be so short that if demand for product
increases, the old firm can use their existing equipments more
intensively but new firms cannot enter into the industry. The
short run normal price is established at a point where the short
period supply curve and the demand curve intersect each other.
The
short run supply curve of the industry is the lateral
summation of the short period marginal cost curves of all the
firms. While the market demand curve is a falling curve
indicating that more is bought when price is low and less when
price is high.
Explanation:
The determination of price and
output in the short run can be explained with the help of the
above diagrams.
Diagram/Figure:
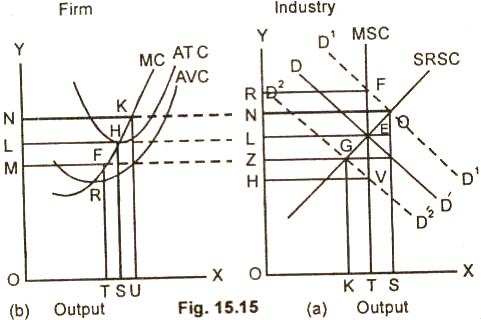
In the fig. 15.15(a) the short run
supply curve (SRSC) of the industry intersects the market demand
curve at point E. The price will be OL and the quantity supplied
OT.
We suppose now that the demand for
the commodity has gone up. The new demand curve D1D1
intersects the market supply curve (MSC) at point F. The price
rise from OL to OR without affecting the output which remains OT
as before. The entrepreneur lured by higher prices will use the
fixed capital equipment more intensively. The old machines will
also be repaired and the production expanded. The new demand
curve then intersects the short period supply curve SRSC at
point Q.
In fig 15.15(b) ON will be the short run normal price which is higher
than the original market price OL but lower than the raised
market price OR. ON thus is the short run normal price of an
industry. This price cannot be changed by the action of an
individual firm as it produces an insignificant portion of the
total supply of the output. It will have to adjust its product
accordingly. At price ON, the firm is earning abnormal profits
because the price is higher than the normal price OL.
If the market demand falls, the new
demand curve D2D2 intersects the market
period supply curve at point G. OZ then is the new equilibrium
market price which is lower than the original OL market price.
The fall in the market price will affect the supply of the
commodity. The firms will reduce their output by decreasing the
variable factors.
Relevant Articles:
|