Long Run Normal Price and the Adjustment of Market Price to the
Long Run Normal Price:
Definition and Explanation:
When we speak of a long period, we do not mean an
interval of time in which we all may be dead. By long run is meant the period in
which the factors of production can be adjusted to changes in demand. The long
run period differs with different industries. In some industries, the
preparation of the plan, the expansion, construction of the new building,
installation of new machinery, training of new labor may take only a few months
and in others, it may take a few years.
In the long run, the price will be determined at
a point where the demand curve and the long run supply curve intersect each
other. The shape of the long run supply curve will, however, be different with
different industries. If the industry is subject to increasing cost, the long
run supply curve will slant upward from left to right. If the industry is
subject to diminishing cost, it will fall downward from left to right. If the
industry is subject to constant cost, it will be parallel to the quantity axis.
Let us examine now the determination of long run
price under the above three conditions and also see as to how the market price
adjusts itself for the long run normal price.
Dynamic Changes and Industry Equilibrium:
(1) Increasing Cost Industry and Long Period
Price Determination:
The long run supply curve in increasing cost
industry slants upward from left to right but the rise is less steep as compared
to short period supply curve. The market price is determined at a point where
the long run supply curve cuts the demand curve as is illustrated below.
Diagram:
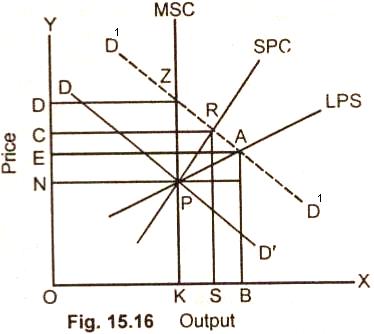
In this fig. 15.16 market supply curve (MSC),
short period supply curve (SPC), long period supply curve (LPSC), pass through
the point P. The market price, short period price and the long run normal price
thus is equal to ON.
Let us suppose that there is once for all increase
in the market demand. The new demand curve D1 D1
intersects the market supply cure, short, period supply curve, and long period
supply curve (LPSC) at points Z, R, A, respectively. The new market price with
be equal to OD, the short period price equal to OC and long period price equal
to OE.
The market price OD is higher than short period
normal price and long run normal price. The short period normal price OC is
lower than the market price but higher than long run normal price. The long run
normal price OE is the lowest of the two but is higher than the original market
price ON. How much the long run price will differ from the market price depends
upon the supply condition in a particular industry. The fact in that the market
price oscillates round the long run normal price.
(2)
Decreasing Cost Industry:
In case of decreasing cost industry, the long run
supply curve will have a negative slope. The price will be determined at a point
where the market demand curve intersects the long period supply curve as shown
below.
Diagram:
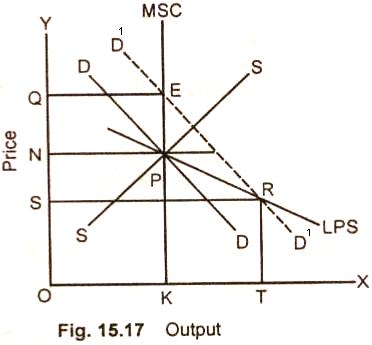
In Fig. (15.17) market supply curve, long period
supply curve and demand curve intersect at point P. ON is the original market
price. If demand rises, the new demand curve D1D1 intersects the market supply, curve at point E and long run supply curve at point R. OQ then will be the new market price and so the long run normal price. The long run normal
price OS is now lower than the original market price ON. The market supply increases from OK to OT in the long run.
(3) Constant Cost Industry:
If the industry is subject to constant cost, the
long run supply curve will be a horizontal straight line parallel to the base
axis.
Diagram:
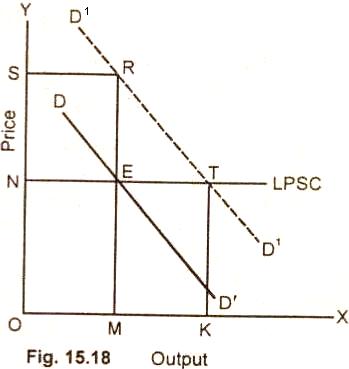
In Fig. 15.18 long period supply curve, market supply curve and the market demand curve pass through point E, ON is thus the
original! market price. If demand rises, the new market price will be higher than the original market price. It is OS in the diagram. In the long run, however, the price falls to
ON because the long period supply curve is a horizontal straight line. The quantity supplied increases from OM to OK.
We, therefore, conclude by saying that the long run normal price will be higher than, lower than or remains equal to the original market price depending open the additional supply which can be acquired according to the changed
conditions in the long run.
Relevant Articles:
|